A prenote or prenotification is a zero dollar payment to validate the account and routing details of a bank account before debiting or crediting it.
To understand how a prenote works, let's take an example where prenotes could be used frequently. When you're setting up a way to pay your utility bill automatically, the utility company could use a prenote to validate your account before debiting it every month. They'll send an ACH prenote to validate your bank account before processing your first automatic payment.
Prenotes are an alternative way to verify bank account information instead of using micro-deposit based verification or account data aggregators like Plaid. The advantage of using prenote account verifications is they don’t require your counterparty to take any action to verify their account. They also don’t require that counterparty to share sensitive information like their username and password for their bank account. The downside is that prenote account verifications take about 3 days to complete.
How do prenotes work?
Prenotes are essentially test transactions that you can make without using real funds.
To send a prenote, all you need to do is make a $0 ACH credit to the counterparty’s bank account. The prenote is considered successful if you don’t receive an ACH Return or Notification of Change related to it from the counterparty’s bank. If the prenote is not successful, you’ll need to use the information in the return code or NOC code to update the bank account details before sending another prenote.
Prenote vs direct deposit
Direct deposit is a payment method where funds are transferred right into the recipient's bank account of choice. The relationship between direct deposits and a prenote is simple; the prenote (or pre-notification) is used to verify the recipient's bank account. Once the prenote account verification is complete and deemed successful, the recipient's bank account is approved for direct deposit and funds can be deposited and accessed.
How long is a prenote period?
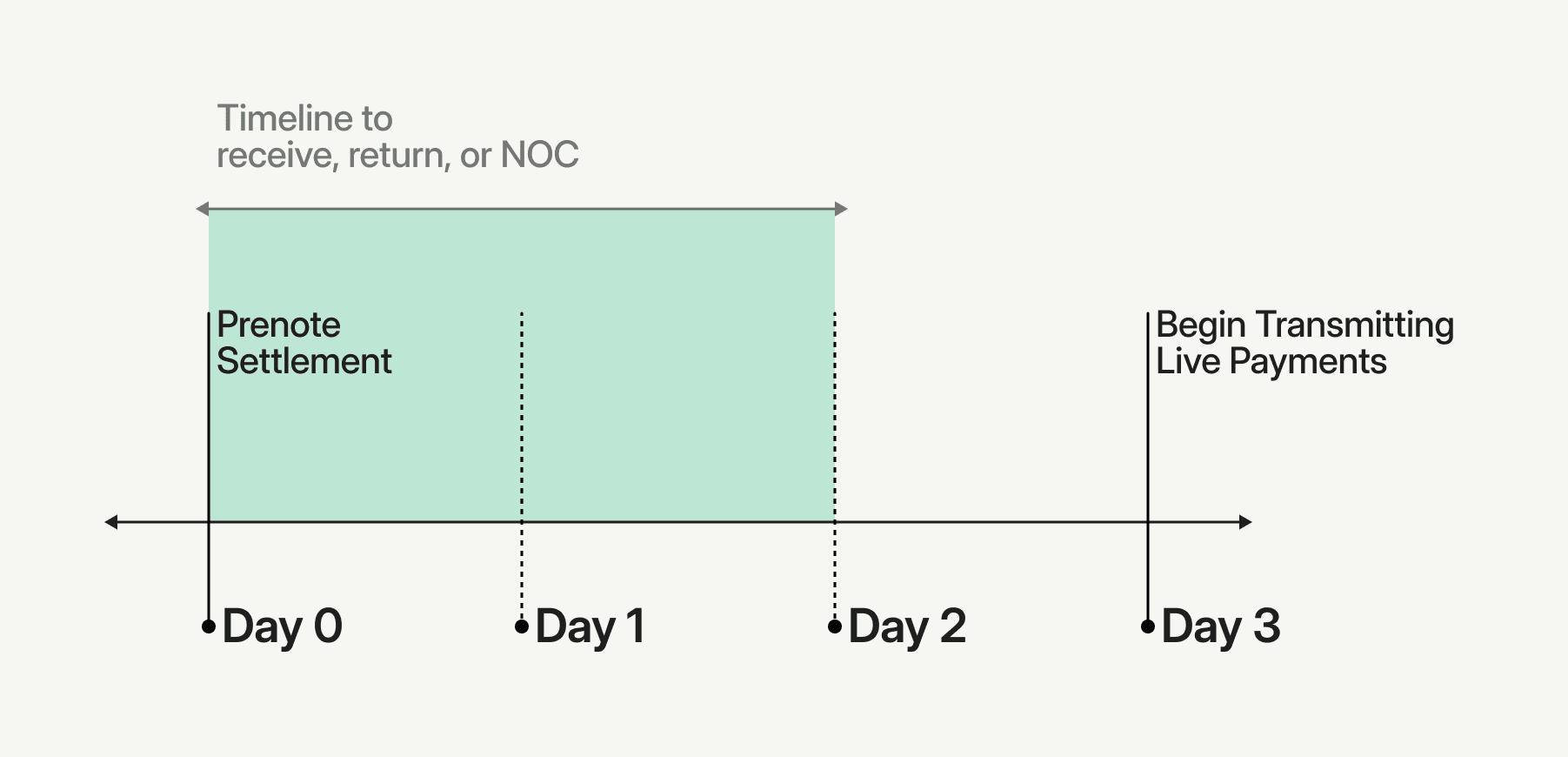
The typical timeline for an ACH prenote is outlined below. So, for example, if you initiate a prenote on a Monday before your bank’s ACH cut-off time, you can start making payments on Thursday provided the prenote did not result in an ACH Return or Notification of Change.
Do other payment methods support prenotes?
Today, prenotes are specific to ACH. Other payment methods like wire transfers and RTP rely on alternative methods for validating account information.
Modern Treasury customers can use the Routing Number API to validate routing information. It supports validating information for multiple payment methods like ACH, Wire Transfer, RTP and SEPA to name a few.
To learn more about bank account verification, take a look at these articles:
Learn
ACH (Automated Clearing House) is a payment processing network that’s used to send money electronically between banks in the United States.
ACH APIs enable companies with high transaction volumes to write software that automates payments over the ACH network.
An ACH credit refers to the process of electronically depositing, or “pushing,” funds into a bank account using ACH.
In an ACH debit, funds are electronically withdrawn, or “pulled,” from a bank account using ACH.
A Notification of Change (NOC) is used to notify the sender of an ACH payment to correct or change information related to a customer’s bank account.
A return is a credit or debit entry initiated by the Receiving Depository Financial Institution (RDFI) that returns a previously originated payment to the Originating Depository Financial Institution (ODFI).
ACH return codes identify the reason an ACH payment was returned by the recipient's bank. They make it easier to spot and resolve payment failures.
An ACH reversal refers to an erroneous ACH payment that a payment originator requests to take back, or reverse.
Credits and debits are two kinds of ACH transactions. Whereas a credit involves depositing, or “pushing,” funds into a bank account, for a debit, funds are withdrawn, or “pulled,” from an account.
FedACH is the automated clearing house (ACH) service of the Federal Reserve Banks.
Part of the FedACH system, FedGlobal ACH offers low-cost and efficient cross-border ACH payments.
The two kinds of financial institutions in the ACH network are ODFIs (Originating Depository Financial Institution) and RDFIs (Receiving Depository Financial Institutions).
A Standard Entry Class or SEC code is a three letter code that describes how a payment was authorized by the consumer or business receiving an ACH transaction.
US companies moving money internationally will likely weigh the pros and cons of SWIFT vs. Global ACH when it comes to attributes like speed and cost.
Payment rails are the underlying systems and networks that facilitate the movement of funds between parties in financial transactions.
ACH (Automated Clearing House) is a payment processing network that’s used to send money electronically between banks and financial institutions in the United States.
An electronic funds transfer (EFT), also known as a direct deposit, is the digital transfer of money between bank accounts. As digital transfers, they reduce the need for manual input and paper documents.
Global ACH can help companies move money from US-domiciled accounts across borders using local rails. Learn how and when to use this payment rail.
A Request for Payment (RFP) is an ACH Network message that can be used by businesses to send electronic invoices to their customers.
Same-Day ACH is an improvement to the ACH network that allows the processing of credit, debit, and return transactions several times a day.
A pre note or prenotification is a zero dollar payment to validate the account and routing details of a bank account before debiting or crediting it.
An International ACH Transfer—also known as Global ACH—is an ACH payment made cross-border from a US-domiciled account.