Part of the FedACH system, FedGlobal ACH offers low-cost and efficient cross-border ACH payments.
What is FedGlobal ACH?
FedACH is the automated clearing house (ACH) service of the Federal Reserve Banks. As one of two primary ACH operators in the US, the FedACH system processes most commercial-bank-based ACH transactions. The Federal Reserve System (aka the “Fed”), composed of 12 banks and 24 branches, is the central banking system of the US government. FedACH acts as its ACH payment operator and handles millions of transactions each day.
FedGlobal ACH credit payments can be sent to 33 countries worldwide, plus ACH debit payments are available to Canada.

FedGlobal ACH Payments are designed to help those already using the FedACH service expand their global payment options by providing cost-effective, flexible, and easy-to-use cross-border ACH payments. There are three ways to make a FedGlobal ACH transaction.
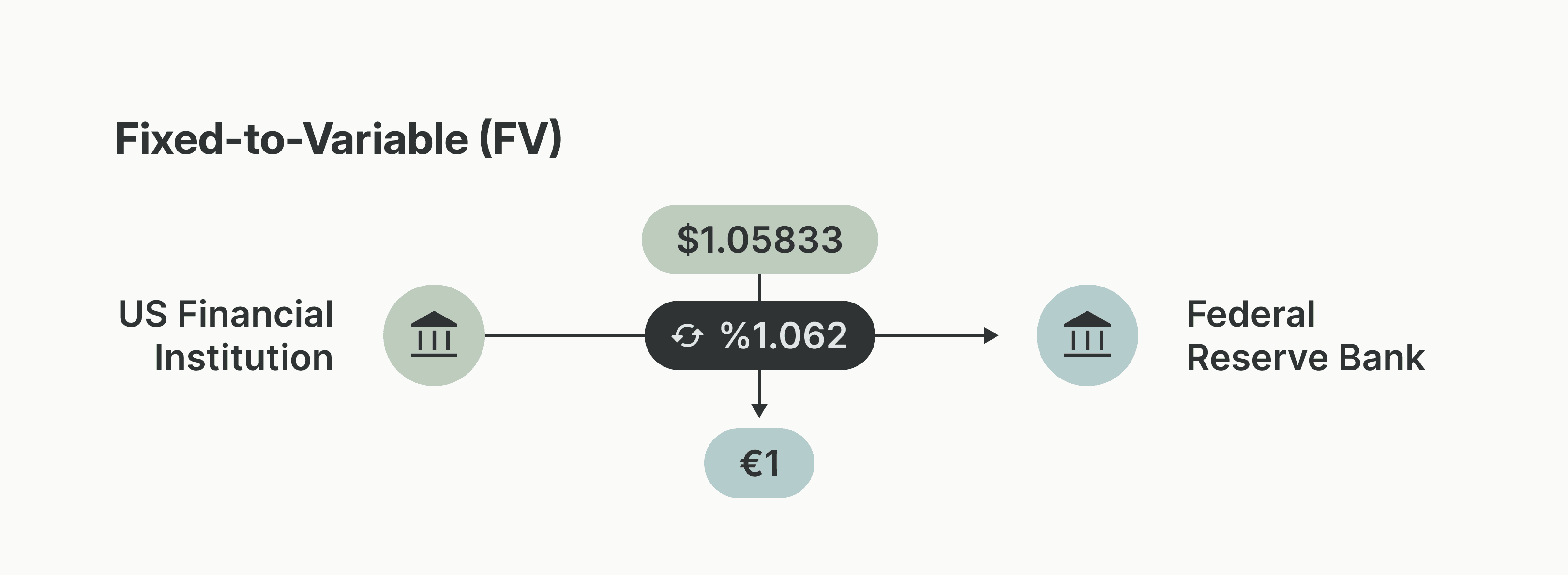
Fixed-to-Variable USD to Foreign Currency
In a fixed-to-variable FedGlobal ACH transaction US dollars are converted to a variable amount of foreign currency based on the exchange rate between USD and the destination country’s currency. Settlement between the US financial institution and the Federal Reserve Bank is in USD.
Fixed-to-Fixed (FF) USD to USD
In this type of FedGlobal ACH transaction, the payments are sent and received in US dollars. Settlement between the US financial institution and the Federal Reserve Bank is, again, in USD.

Fixed-to-Fixed (F3X) Foreign Currency to Foreign Currency
Payments are both transferred and received in foreign currency. The foreign exchange rate and settlement is managed and processed by participating U.S. financial institutions and the respective foreign gateway operators via their foreign correspondent banks.

Currently, there are different service areas for each of the three different FedGlobal ACH transaction types.

Learn
ACH (Automated Clearing House) is a payment processing network that’s used to send money electronically between banks in the United States.
ACH APIs enable companies with high transaction volumes to write software that automates payments over the ACH network.
An ACH credit refers to the process of electronically depositing, or “pushing,” funds into a bank account using ACH.
In an ACH debit, funds are electronically withdrawn, or “pulled,” from a bank account using ACH.
A Notification of Change (NOC) is used to notify the sender of an ACH payment to correct or change information related to a customer’s bank account.
A return is a credit or debit entry initiated by the Receiving Depository Financial Institution (RDFI) that returns a previously originated payment to the Originating Depository Financial Institution (ODFI).
ACH return codes identify the reason an ACH payment was returned by the recipient's bank. They make it easier to spot and resolve payment failures.
An ACH reversal refers to an erroneous ACH payment that a payment originator requests to take back, or reverse.
Credits and debits are two kinds of ACH transactions. Whereas a credit involves depositing, or “pushing,” funds into a bank account, for a debit, funds are withdrawn, or “pulled,” from an account.
FedACH is the automated clearing house (ACH) service of the Federal Reserve Banks.
Part of the FedACH system, FedGlobal ACH offers low-cost and efficient cross-border ACH payments.
The two kinds of financial institutions in the ACH network are ODFIs (Originating Depository Financial Institution) and RDFIs (Receiving Depository Financial Institutions).
A Standard Entry Class or SEC code is a three letter code that describes how a payment was authorized by the consumer or business receiving an ACH transaction.
US companies moving money internationally will likely weigh the pros and cons of SWIFT vs. Global ACH when it comes to attributes like speed and cost.
Payment rails are the underlying systems and networks that facilitate the movement of funds between parties in financial transactions.
ACH (Automated Clearing House) is a payment processing network that’s used to send money electronically between banks and financial institutions in the United States.
An electronic funds transfer (EFT), also known as a direct deposit, is the digital transfer of money between bank accounts. As digital transfers, they reduce the need for manual input and paper documents.
Global ACH can help companies move money from US-domiciled accounts across borders using local rails. Learn how and when to use this payment rail.
A Request for Payment (RFP) is an ACH Network message that can be used by businesses to send electronic invoices to their customers.
Same-Day ACH is an improvement to the ACH network that allows the processing of credit, debit, and return transactions several times a day.
A pre note or prenotification is a zero dollar payment to validate the account and routing details of a bank account before debiting or crediting it.
An International ACH Transfer—also known as Global ACH—is an ACH payment made cross-border from a US-domiciled account.